Java| 03 无限循环、跳转控制语句、数组等
Java| 03 无限循环、跳转控制语句、数组等
NGX无限循环(死循环)
for循环
1 | for(;;){ |
while循环
1 | while(true){ |
do while循环
1 | do{ |
跳过控制语句
Idea快捷补全
在idea中输入5.fori会自动补全以下代码:
1 | for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { |
continue
详细用法: continue;指如果条件成立则退出本次循环, 继续下一个循环.
1 | class Main { |
运行结果:
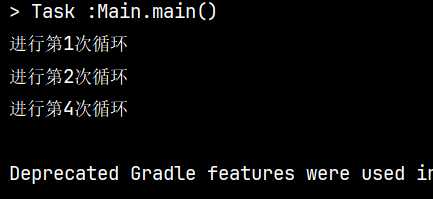
可以看到它跳过了一次循环
break
与continue不同, break则是结束整个循环.
1 | class Main { |
只需将continue简单的改为break即可.
运行结果:
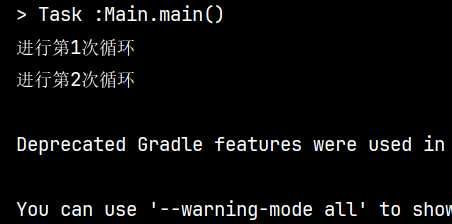
可以清楚的看到循环只进行了两次.
练习: 逢七过
游戏规则: 从任意一个数字开始, 当你报的数字是7或者是7的倍数时, 都要说过.
题目: 使用Java程序在控制台中打出1-100之间满足逢七过游戏的数据.
分析及回答
思路: 先获取1-100个数字, 然后判断每一个数字, 如果符合标准就输出过, 不符合就输出原数字.
完整代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 循环遍历1到100的所有数字
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
// 检查数字是否满足特定条件
if (i % 10 == 7 || i / 10 % 10 == 7 || i % 7 == 0) {
// 如果满足条件,打印"过"并跳过当前数字的后续处理
System.out.println("过");
continue;
}
// 如果不满足条件,正常打印数字
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}运行结果:

数组
数组指的是一种容器, 可以用来存储同种数据类型的多个值.
初始化指的是在内存中, 为数组容器开辟空间, 并将数据存入空间的过程.
数组的定义及初始化
定义格式
格式一
1 | // 数据类型 [] 数组名; |
格式二
1 | // 数据类型 数组名 []; |
静态初始化
1 | // 数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[]{元素1, 元素2, 元素3, ...} |
数组的地址值
数组的地址值表示数组在内存中的位置。
格式含义
[: 表示这是一个数组。
I: 表示数据类型是int型。
@:表示间隔符号,固定格式。
776ec8df: 数组的真实地址值,十六进制。
访问数组元素
索引
也叫做下标、角标;从0开始逐步+1增长,连续不间断。
1 | // 获取数组元素:数组名[索引] |
在这个例子中,1的索引是0,所以要输出1就要得到第一个数据并输出。
1 | int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; |
在这里将10添加到数组array的索引0中. 添加数据后, 原来在此索引中的数据就不存在了.
1 | int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; |
遍历数组
将数组中所有的内容取出来, 可以进行(输出, 求和, 判断…)等操作
1 | int[] array = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55}; |
可以利用for循环来完成此次操作. 但这是知道数组长度且保持不变的遍历方法. 如果长度变了, 那么for循环的结束条件也要变.
所以, 在Java中可以使用数组名.length来调用一个关于数组的长度属性.
1 | int[] array = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55}; |
注意是int i = 0; i < array.length; i++而不是int i = 0; i <= array.length; i++.否则会出现数组越界的问题.
注意: i依次表示数组里面的每一个索引; array[1]表示数组里每一个元素.
idea自动补全数组遍历代码方式: array.fori
小练习: 数组求和
分析及作答
1
2
3
4
5
6
7int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
sum = sum + array[i];
}
System.out.println(sum);
// 最终输出 15
小练习: 输出1-10能被3整除的数字
分析及作答
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化一个整数数组,包含1到10的数字。
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
// 初始化一个变量用于累计能被3整除的元素的数量。
int sum = 0;
// 遍历数组中的每个元素。
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// 检查当前元素是否能被3整除。
if(array[i] % 3 == 0){
// 如果能被3整除,增加计数。
sum++;
}
}
// 输出能被3整除的元素的数量。
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
// 输出 3
小练习: 变化数据
需求: 定义一个数组, 存储1-10个数. 遍历数组得到每一个元素. 要求如果是奇数, 则将当前数字扩大两倍, 如果是偶数, 则将当前数字变成二分之一
分析及作答
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化一个整数数组,包含1到10的整数。
// 创建1-10个元素的数组
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
// 遍历数组,对每个元素进行处理。
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 判断当前元素是否为偶数。
// 判断
if (arr[i] % 2 == 0) {
// 如果是偶数,将其除以2。
arr[i] = arr[i] / 2;
} else {
// 如果是奇数,将其乘以2。
arr[i] = arr[i] * 2;
}
}
// 再次遍历数组,打印处理后的每个元素。
// 输出
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
动态初始化
动态初始化:初始化时只指定数组长度,由系统为数组分配初始值。
格式: 数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[数组长度];
举个例子: int[] myArray = new int[10];
这是一个简单的示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = new String[2];
arr[0] = "Hello";
arr[1] = "World";
System.out.println(arr[0] + " " + arr[1]);
}
}
默认初始化规律
整型(byte,short,int,long):默认初始化值为 0。
浮点型(float,double):默认初始化值为 0.0。
字符型(char):默认初始化值为 空格(' ',对应Unicode编码 \u0000)。
布尔型(boolean):默认初始化值为 false。
引用数据类型(如String):默认初始化值为 null。
和静态初始化的区别
静态初始化是在编码时就确定了数组的内容,而动态初始化则提供了更多的灵活性,允许在运行时确定数组的大小和内容。
- 静态初始化详细特点
在声明数组的同时,你需要指定每个元素的值。
数组的长度由初始化时提供的元素数量决定。
适用于你已经知道所有元素值的情况。
例如:
1
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
这里,
numbers数组被创建并初始化为具有5个元素的数组。
- 动态初始化详细特点
- 动态初始化:
你只指定数组的长度,元素的值将被设置为默认值。
数组的长度在声明时由你指定。
适用于你只知道数组的大小,但不知道具体元素值的情况。
例如:
1
int[] numbers = new int[5];
这里,
numbers数组被创建为长度为5的数组,所有元素默认初始化为0。
- 动态初始化:
常见操作
求最值
已知数组元素为{33, 5, 17, 90, 1}, 求该数组最大值并输出到控制台.
分析及作答
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化一个整数数组
// 定义数组
int[] arr = {33, 5, 17, 90, 1};
// 假设数组的第一个元素为最大值
// 定义max变量, 临时认为索引0是最大值
int max = arr[0];
// 遍历数组以查找实际的最大值
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 如果当前元素大于假设的最大值,则更新最大值
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
// 打印最大值
System.out.println("最大值为:" + max);
}
}
Java内存分配
- 栈 方法运行时使用的内存,比如
main方法运行,进入方法栈中执行 - 堆 存储对象或者数组,
new来创建的,都存储在堆内存 - 方法区 存储可以运行的
class文件 - 本地方法栈 JVM在使用操作系统功能的时候使用,和我们开发无关
- 寄存器 给CPU使用,和我们开发无关
方法
把一些代码打包在一起,用到的时候就调用。
方法的格式
最简单的方法定义和调用
1 | // 定义 |
注意:方法必须先定义后调用。
范例:
1 | public class Main { |
带参数的方法定义和调用
形参:全称形式参数,是指方法定义中的参数。
实参:全称实际参数,方法调用中的参数。
1 | // 定义 |
注意:调用时参数必须与定义的参数一一对应。
范例:
1 | public class Main { |
带返回值的方法定义和调用
1 | public static 数据类型 方法名(参数1, 参数2, ...){ |
范例:
1 | public class Main { |
方法的重载
在同一个类中,定义了多个同名的方法,这些同名的方法具有同种的功能。
每个方法都具有不同的参数类型或参数个数,这些同名的方法,就构成了重载关系。
1 | public class Main { |
练习:求数组最大值
设计一个方法求数组最大值,并返回最大值。
1 | public class Main { |
练习:判断是否存在
定义一个方法判断数组中的某一个数是否存在,将结果返回给调用处。
1 | public class Main { |
这里使用增强型for循环遍历列表。
注意:增强型for循环列表的每一项是 i ,而传统for循环的每一项是 arr[i] 。
练习:复制数组
将数组arr中索引from(包含from)开始,到索引to(不包含to)的元素复制到新数组中,返回新数组。
1 | public class Main { |
练习:卖飞机票
机票价格按照淡季旺季、头等舱和经济舱收费、输入机票原价、月份和头等舱或经济舱。
按照如下规则计算机票价格:旺季(5-10月)头等舱9折,经济舱8.5折,淡季(11月到来年4月)头等舱7折,经济舱6.5折。
传统写法:
1 | import java.util.Scanner; |
简洁方法:
1 | import java.util.Scanner; |